The Japan Patent Office (JPO) sided with Kumamon and declared invalidation of trademark registration no. 5997141 for a bear-like design mark due to a likelihood of confusion with Kumamon.
[Invalidation case no. 2019-890004, Gazette issue date: February 28, 2020]
KUMAMON
Have you ever heard of “Kumamon”?
Nowadays, we are accustomed to see there are many organizations that create and use mascots to further their brands. Kumamon is a cuddly character with its pitch-black fur, red cheeks and white eyes designed as the official mascot (see below) of the Kumamoto Prefecture, a small prefecture in western Japan.
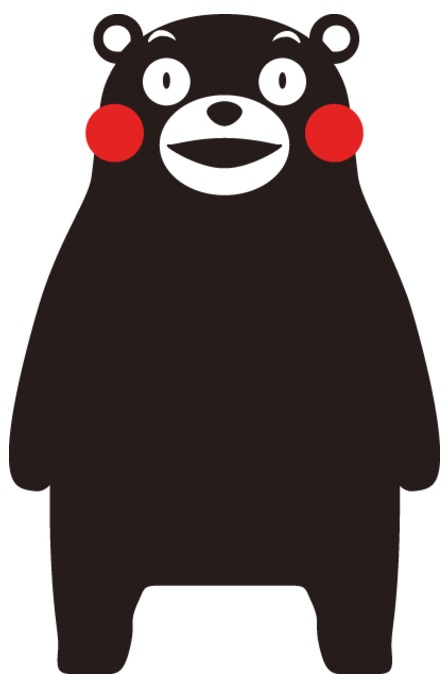

Kumamon made its debut in 2011 as part of a tourism promotion campaign for the Kyushu high-speed railway line. At the time a wave of local municipalities and companies sought to use ‘yuru-kyara’, or ‘relaxing characters’, to promote local products and attractions. Kumamon was hired as a part-time civil servant at Kumamoto before being elevated to sales manager. Such topics generated headlines and helped push Kumamon’s popularity beyond Kumamoto.

As an iconic symbol of ‘relaxing characters’, Kumamon has become a social and cultural phenomenon nationwide. Sales of goods using the Kumamon mascot topped 150 billion yen ($1.4 billion) in 2018.
To protect and promote the mascot, the Kumamoto Prefecture has registered its figurative image reproduced in 2D for various classed of goods and services in Japan as well as neighboring countries.
Disputed Mark
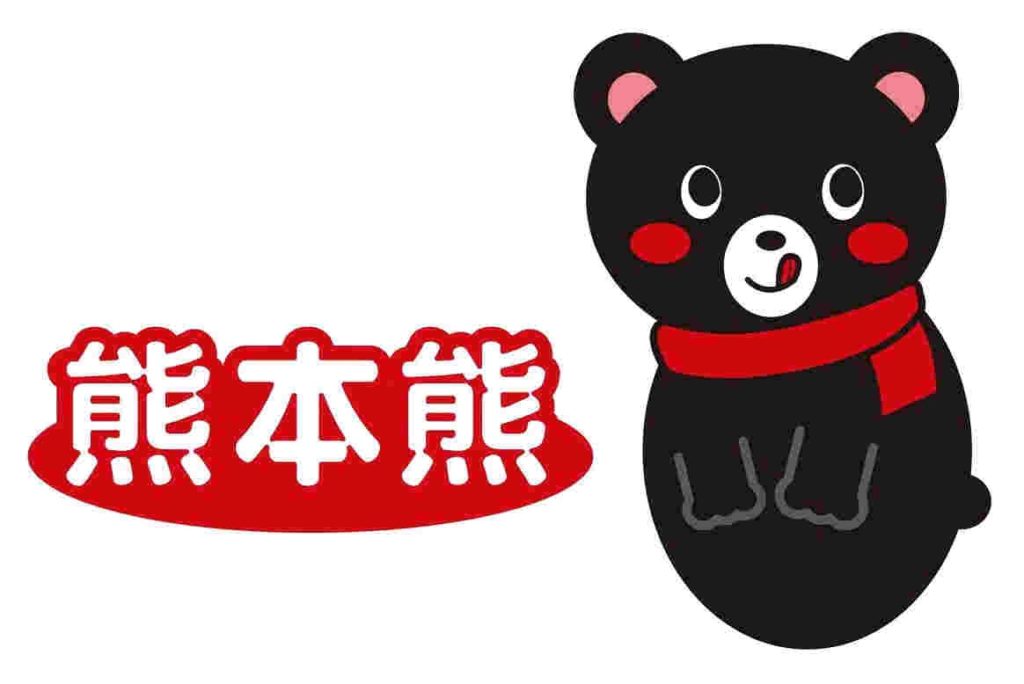
On March 21, 2017, Unique Design Company Limited (Belize) , sought to register the mark consisting of a bear-like design and three Chinese characters “熊本熊” which mean Kumamoto’s bear (see below) to be used on goods in class 11. The JPO granted protection of opposed mark on October 27, 2017.

Invalidation Trial
To challenge the validity of disputed mark, on January 25, 2019, the Kumamoto Prefecture filed an invalidation action to the JPO based on Article 4(1)(vi), (vii), (xi), (xv) and (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law. Kumamoto Prefecture argued that the figurative element of disputed mark closely resembles to the Kumamon character well-known for the official mascot of the Kumamoto Prefecture from appearance. Besides, the literal element of disputed mark gives rise to a similar meaning related to the Kumamoto Prefecture and Kumamon. If so, disputed mark as a whole shall be invalid due to a likelihood of confusion with Kumamon.
JPO Decision
The Invalidation Board of JPO found that:
- Unquestionably, Kumamon has acquired a remarkable degree of reputation and popularity nationwide as the official mascot of the Kumamoto Prefecture well before the filing date of disputed mark through continuous activities, promotions, and actual use on various goods since 2011. In addition, it becomes public among relevant consumers that the literal element of disputed mark “熊本熊” gets to be known as a Chinese name of Kumamon in China and neighboring countries.
- Since Kumamon has distinctive features visually different from wild bear, the mascot shall be deemed unique, creative, and impressive in itself.
- From appearance the bear-like design of disputed mark is confusingly similar to Kumamon. It gives rise to a similar meaning to Kumamon, the mascot originated from bear in the Kumamoto Prefecture. Likewise, the literal element of disputed mark gives rise to the same meaning. If so, both marks are considered highly similar.
- Due to free-use policy for brand promotion to domestic merchants (Kumamoto lets domestic companies use the character for free, but charges a license fee of a few percent on product sales by foreign companies), Kumamon mascot has been commercially used on wide range of goods over 10,000 items. 7-year cumulative sales exceed 510 billion JP-yen. If so, disputed goods in class 11, e.g. oil stoves, heaters, pocket warmers, electric foot warmers, shall be closely associated with the Kumamon goods in channels and consumers.
Based on the above findings, the Board concluded that relevant consumers and traders are likely to confuse disputed mark with Kumamon or misconceive a source from any entity systematically or economically connected with the Kumamoto Prefecture. Thus, disputed mark shall be invalidated in violation of Article 4(1)(xv) of the Trademark Law.