The Japan Patent Office (JPO) sided with Industria de Diseño Textil, SA (INDITEX), owner of the fashion brand “ZARA” in an invalidation action against Japanese TM Registration no. 6110359 for word mark “Zarbleu” in class 25 by finding a likelihood confusion with “ZARA”.
[Invalidation case no. 2019-890038, Gazette issued date: August 28, 2020]
Zarbleu
Disputed mark “Zarbleu” was applied for registration by a Chinese corporation on January 24, 2018, by designating sweaters, shirts, trousers, outers, skirts, dresses, T-shirts, underwear, headgear, gloves, coats, and other clothing in class 25, and registered on December 28, 2018, without confronting with office action from the JPO.
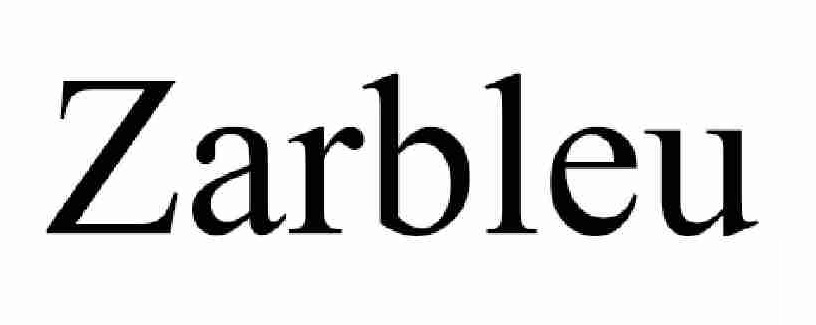
Invalidation action by Inditex
INDITEX, one of the world’s largest fashion retailers and owner of the fashion brand “ZARA”, filed an invalidation action on July 20, 2019, and claimed “Zarbleu” shall be retroactively invalidated in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) of the Japan Trademark Law by citing senior trademark registrations for word mark “ZARA” in relation with clothing in class 25 and 35.
Article 4(1)(xv) prohibits registering a trademark which is likely to cause confusion with the business of other entities.

INDITEX argued, given “ZARA” has acquired a remarkable reputation among relevant consumers and the close resemblance between the marks and goods, relevant consumers are likely to confuse or misconceive opposed mark with “ZARA”.
JPO Decision
It would not surprise us that the JPO Invalidation Board admitted a high degree of reputation and popularity of “ZARA” among relevant consumers and traders as a source indicator of INDITEX in connection with clothing based on the facts that (i) “ZARA” launched fashion business in Japan since 1998 and increased the number of its stores in Japan to 100 as of December 2019, (ii) worldwide sales in excess of EUR 18 billion. (iii) ZARA has been ranked No.24(2017), No.25(2018) on Interbrand’s list of the most valuable global brands.
Astonishingly, the Board found a certain degree of similarity between “ZARA” and “Zarbleu” by stating that relevant consumers have a tendency to pay higher attention to the prefix of a mark and “Zarbleu” incorporates the same prefix “Zar” with “ZARA” which has acquired a high degree of reputation among the consumers in connection with clothing.
In addition, addressing sufficient strength of the ZARA mark as a fanciful term and close relatedness of goods in dispute, the Board concluded that relevant consumers and traders are likely to confuse clothing bearing the disputed mark “Zarbleu” with ZARA or misconceive a source from any entity systematically or economically connected with INDITEX. Thus, the disputed mark shall be invalidated in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) of the Trademark Law.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO decided in favor of INDITEX and declared invalidation of the disputed mark “Zarbleu”.