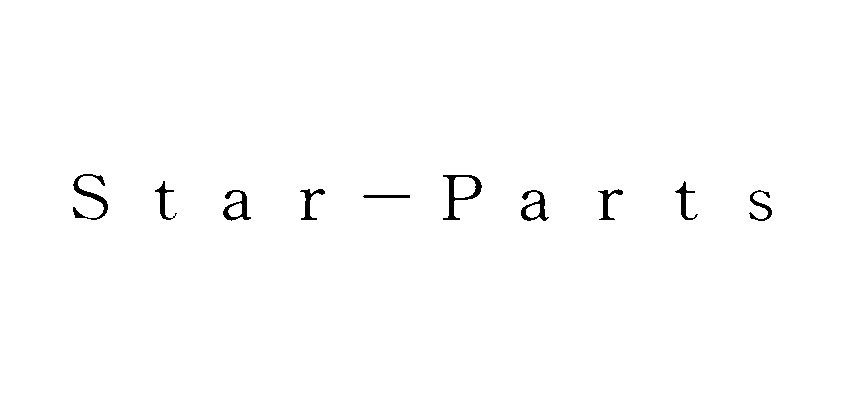The Japan Patent Office (JPO) rejected Armani’s opposition against Japanese TM Reg no. 6214148 for V-shaped device mark on apparels in class 25.
[Opposition case no. 2020-900093, Gazette issued date: March 26, 2021]
Opposed mark
The mark in dispute (see below) was filed on April 3, 2019, for use on various goods in class 9, 25, and 28 by ASAHI Golf Co., Ltd.
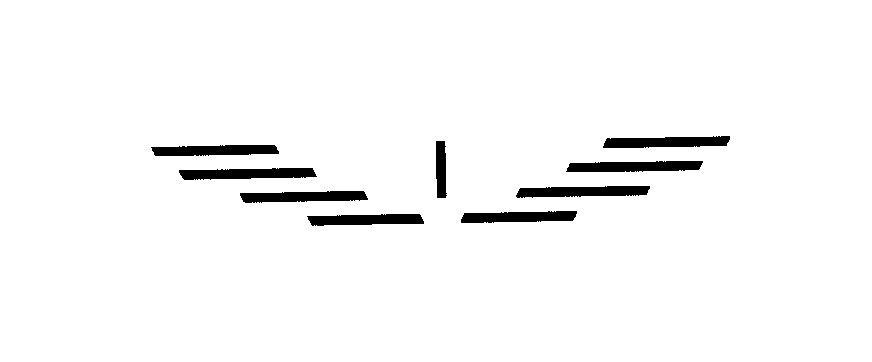
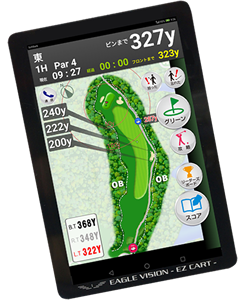
Apparently, the applicant uses the opposed mark on its Golf Cart GPS “EAGLE VISION -EZ CART.”
The JPO admitted the registration of the opposed mark on January 7, 2020 and published for opposition on January 28, 2020.
Armani Opposition
On March 30, 2020, Giorgio Armani S.p.A. filed an opposition with the JPO, based on its senior IR no. 695685 and “Eagle” logo.

Armani considered the opposed mark shall be cancelled in contravention of Article 4(1)(x), (xi), (xv) and (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law because the opposed mark is similar to Armani’s Eagle marks. Besides, relevant consumers are likely to confuse especially when the opposed mark is used on apparels in class 25.
Allegedly, Armani launched business in Japan and founded a Japanese local subsidiary in 1987. Presently, it operates 64 stores in Japan. Armani’s Eagle marks have been used on various fashion items in conjunction with “Giorgio Armani”, “Armani Jeans”, “Armani Junior”, “Emporio Armani”, and “EA7 Emporio Armani.” Annual goods sales exceed JPY 40 billion worldwide, JPY 8 billion in the marketplace of Japan. Armani spends more than JPY 20 billion for advertisement every year around the globe. Approximately 60 million goods have been delivered for sale each year. To bolster the allegations, Armani produced some advertisements, invoices, annual reports, magazines, catalogues and other evidence in order to prove actual use of Armani’s Eagle marks in Japan.
Board decision
The Opposition Board of the JPO had concluded that insufficient evidence had been submitted to objectively support the assumption of a well-known mark. Because of it, the Board denied a certain degree of popularity and reputation of Armani’s Eagle marks among relevant consumers in Japan.
As to the similarity of the marks, the JPO held that the opposed mark would be anything but associated with an eagle from its configuration. If so, both marks are visually distinguishable. Besides, both marks would not give rise to any specific meaning and pronunciation at all. Thus, the Board held that the marks are deemed dissimilar.
Even if the goods in dispute are closely associated with Armani’s business, given a low level of similarity between the marks and insufficient evidence to assume famousness of Armani’s Eagle marks, the Board found no reason to believe the opposed mark would cause confusion with Armani when used on apparels in class 25.
Based on the foregoing, the Board decided opposed mark is not subject to Article 4(1)(x), (xi), (xv) and (xix) of the Trademark Law and dismissed the opposition entirely.
I believe Armani’s Eagle marks have already acquired a high degree of reputation in Japan. Should Armani produce adequate and persuasive evidence with the JPO regarding actual and substantial use of the mark in Japan, the outcome would be different.