The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed trademark opposition against wordmark “REDHOT” written in Katakana character opposed by The French’s Food Company LLC who owns senior trademark “REDHOT” and “FRANK’S REDHOT” in class 30.
[Opposition case no. 2020-900289, Gazette issued date: June 25, 2021]Opposed mark “REDHOT”
Opposed mark, consisting of the word “REDHOT” written in Japanese Katakana character (see below), was filed by Kentucky Fried Chicken Japan (KFC) for use on fried chicken, meat, processed meat products, and other goods in class 29 and hamburgers, hot dog sandwiches, bread rolls, and other goods except for seasonings and spices in class 30 with the JPO on November 6, 2018 (TM Application no. 2018-142676).
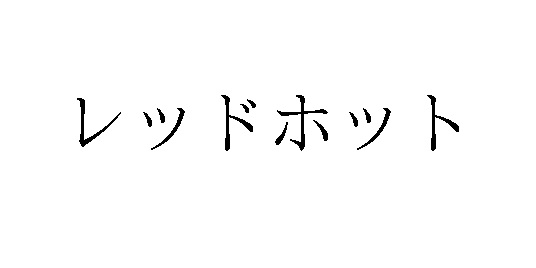
KFC Japan has begun selling the “Red Hot Chicken”, red and white pepper with a touch of habanero, giving it a crisp, spicy flavor and the taste of domestic chicken in limited quantities since 2004.

FRANK’S REDHOT
The French’s Food Company LLC, an owner of the #1 brand of hot sauce “Frank’s RedHot” in America, filed an opposition on November 2, 2020.
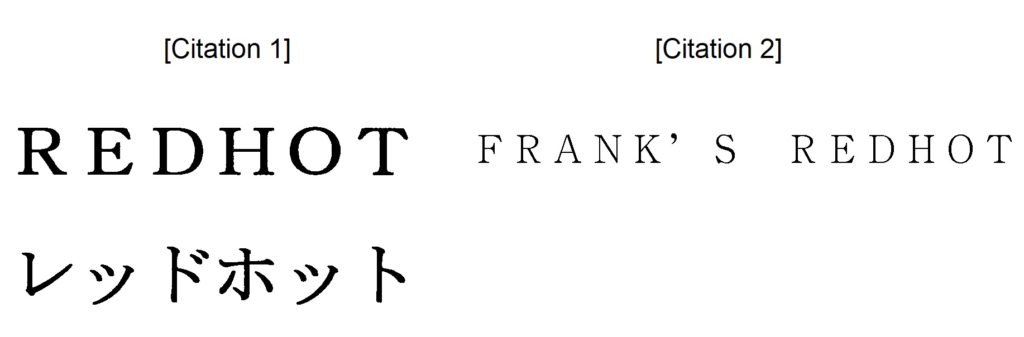
Opponent argued that the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(xi) and (xv) because of similarity to senior TM Reg nos. 4723565 and 5523112 for wordmark “REDHOT” on seasonings and spices in class 30 (Citation 1), and a likelihood of confusion with TM Reg no. 5523111 for wordmark “FRANK’S REDHOT” (Citation 2) which has become famous as a source indicator in connection with hot sauce as a result of substantial and continuous use since 1920.
JPO decision
The Opposition Board of JPO found that Article 4(1)(xi) shall not be applicable to the opposed mark.
Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit registering a junior mark that is identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
Since the designated goods, seasonings and spices, of the opposed mark are deemed dissimilar to any other goods belonging to class 30. In so far as respective goods in question are dissimilar, the opposed mark shall not be subject to the article even though the mark is identical with Citation 1.
The Board questioned whether the mark “FRANK’S REDHOT” has acquired a certain degree of reputation and popularity among relevant consumers in Japan by taking account of the produced evidence. The mere fact that the opponent’s hot sauces get to be a popular choice at specific dining restaurants is insufficient to support the famousness of Citation 2 in Japan.
Besides, relevant consumers would be easily able to distinguish the opposed mark with “FRANK’S REDHOT” by means of the distinctive term “FRANK’S” of Citation 2.
Given the low degree of similarity and unproven famousness as a source indicator of the opponent, the Board concluded it is unlikely that relevant consumers would confuse the source of goods bearing the opposed mark with the opponent or Citation 2 from the totality of circumstances, and thus dismissed the opposition entirely.