In a trademark opposition at the Japan Patent Office (JPO), French luxury brand HERMES achieved victory to stop the registration of a word mark “D. KELLY” over bags and pouches in class 18.
[Opposition case no. 2018-900177, Gazette issue date: March 27, 2020]
Opposed mark
Opposed mark, “D.KELLY” was applied for registration on August 25, 2017 by designating bags and pouches in class 18, and published for registration on May 22, 2018 without any office action from the JPO examiner.
Applicant, a Japanese individual, apparently operates brick-and -mortar shops in Japan and on-line shop to promote hand bags, shoulder bags, tote bags, rucksacks/backpacks and other fashion items.
“D.KELLY” is used on the bags and as its shop name.

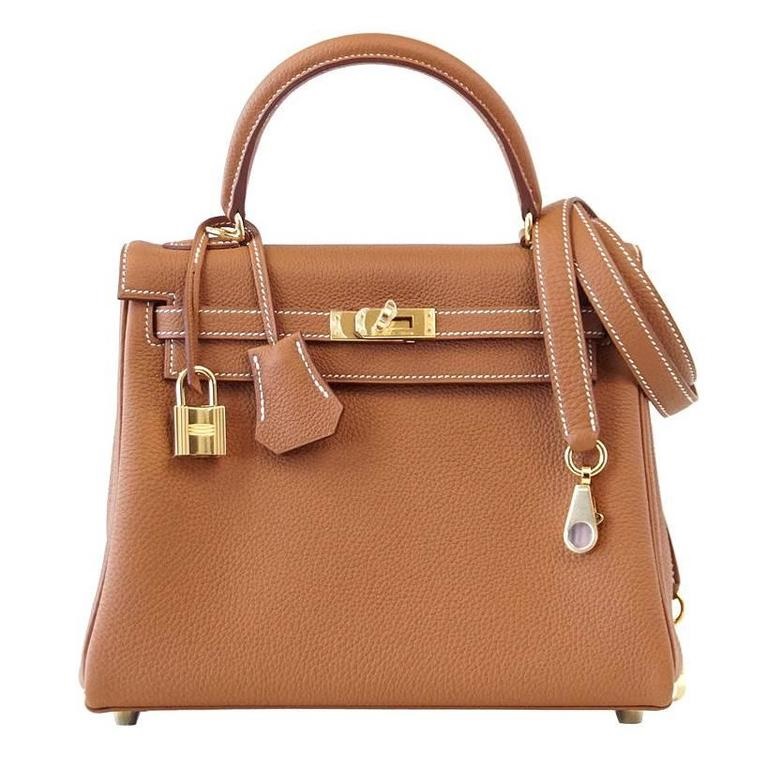
Hermes Kelly Bag
Opponent, HERMES INTERNATIONAL, a French luxury fashion house, claimed that the opposed mark “D.KELLY” shall be liable for cancellation under Article 4(1)(xi) and (xv) of the Japan Trademark Law by citing the Hermes Kelly Bag and an owned senior trademark registration no. 4341534 for word mark “KELLY” in standard character over bags, pouches and other goods in class 18.

Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit from registering a junior mark which is deemed identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
Hermes argued opposed mark is perceived as a combination of “D.” and “KELLLY”. The prefix “D.” per se lacks distinctiveness in relation to the goods in question. The mark as a whole does not give rise to any specific meaning at all. As a consequence, the literal portion of “KELLY” shall play a dominant role as a source indicator. If so, opposed mark is deemed confusingly similar to “KELLY” owned by Hermes. Besides, both marks designate same goods in class 18.
Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entity’s well-known goods or services, to the benefit of brand owner and consumers.
Given a remarkable degree of reputation of Hermes “Kelly” Bag in relation to bags, relevant consumers with an ordinary care would associate “D.KELLY” with Hermes and confuse its source when used on bags and pouches because “KELLY” is not a common surname in Japan and thus the term is more distinctive than “D.”.
JPO decision
The Opposition Board of JPO sided with Hermes and decided to cancel opposed mark by stating that:
- From the produced evidences, Hermes has continuously used the cited mark on bag since 1956, inspired by an icon, Princess Grace Kelly of Monaco. The bag has been advertised or publicized in fashion magazines and internet frequently. Annual sales consecutively reach in the range of JPY 1.6 to 4.6 billion, which amounts 2,000 to 4,000 bags in quantity, for the past fifteen years. The Board admits a high degree of reputation and popularity of opponent mark “KELLY” as a source indicator of Hermes bag.
- The Board considers opposed mark is a compound mark of “D” and “KELLY” placing dot(.) in-between. Since an alphabetical letter “D” lacks distinctiveness, relevant consumers would conceive the portion of “KELLY” as a dominant source indicator. If so, opposed mark may give rise to a meaning of Hermes brand bag, identical pronunciation and appearance with opponent’s mark. It is unquestionable that goods in question belongs to that of the citation.
- Provided that Hermes “Kelly Bag” has been rather known for in a name of “Kelly Bag” than “Kelly”, the Board finds a high degree of similarity between the marks in relation to bags. If so, it is undeniable that relevant consumers and traders are likely to confuse opposed mark with Hermes “Kelly Bag” or misconceive a source from any entity systematically or economically connected with Hermes International.
- Based on the foregoing, opposed mark shall be liable for cancellation based on Article 4(1)(xi) and (xv).