As the year 2025 comes to an end, it is a good time to share the top 10 trademark news in Japan by counting the total number of likes on the Linkedin “Like” Button.
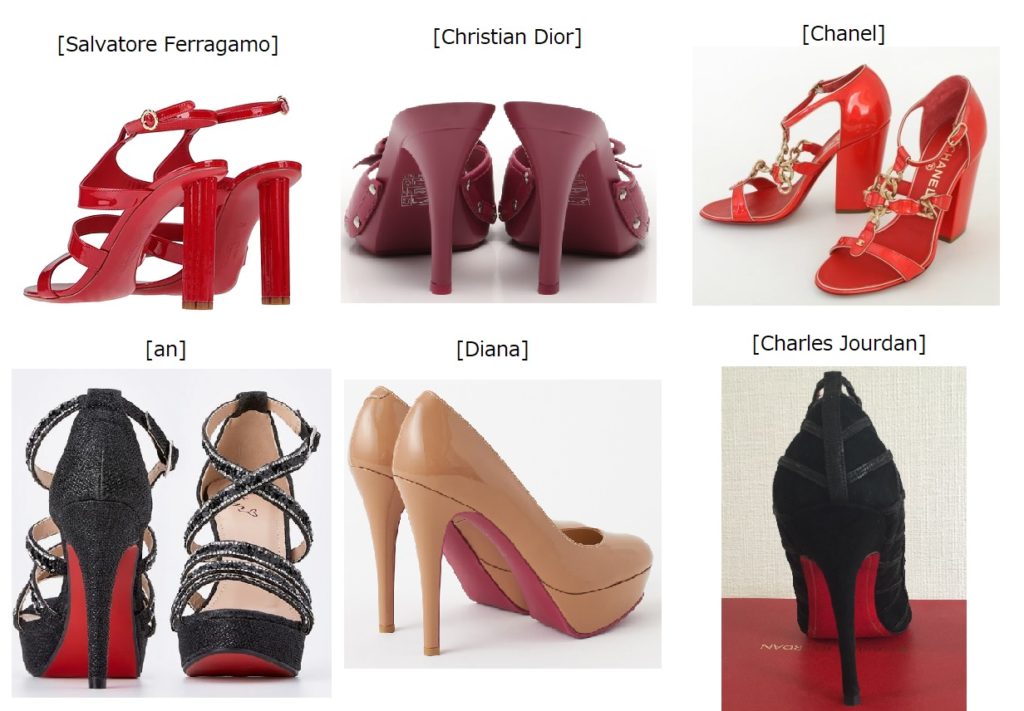
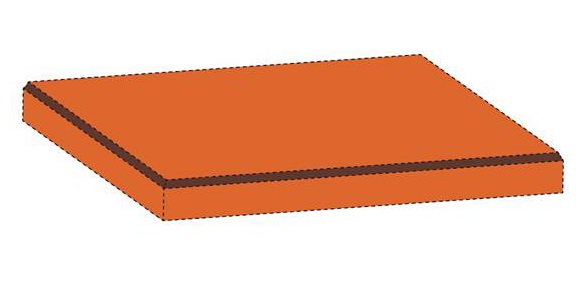
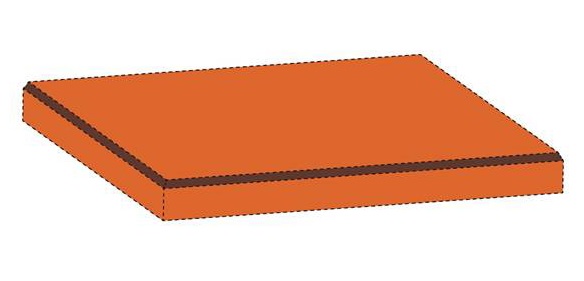
1: JPO Grants TM Registration for 3D Shape of the Popular Pocky Cookie
The Japan Patent Office (JPO) granted trademark registration for the three-dimensional (3D) shape of Ezaki Glico’s iconic “Pocky” cookie, recognizing that the shape had acquired distinctiveness in relation to chocolate confections in Class 30 [TM Reg. No. 6951539].
2: UNIQLO Lost in Trademark Opposition against UNIPRO
UNIQLO lost in its attempt to oppose TM Reg no. 6746724 for the mark “UNIPRO” in class 28 due to dissimilarity and unlikelihood of confusion with a world-famous Japanese clothing brand “UNIQLO”.
3: STARBUCKS Unsuccessful Invalidation Action against Trademark “STARBOSS”
The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an invalidation action claimed by Starbucks Inc. against TM Reg no. 6595964 for wordmark “STARBOSS” in class 32 due to dissimilarity to and unlikelihood of confusion with the world’s largest coffee chain “STARBUCKS”.
4: IP High Court ruling: STARBUCKS vs STARBOSS
The Japan IP High Court did not side with Starbucks Corporation in a trademark dispute between “STARBUCKS” and “STARBOSS”, and affirmed the JPO decision that found “STARBOSS” dissimilar to, and less likelihood of confusion with “STARBUCKS when used on beverages.
5: Trademark dispute: SONY vs SONIMART
The Japan Patent Office (JPO) sided with SONY in a trademark invalidation action against TM Reg no. 6162062 for word mark “SONIMARK” in classes 35 and 42 by finding a likelihood of confusion with famous mark “SONY”.
6: MONSTER STRIKE vs MONSTER ENERGY
The Japan Patent Office (JPO) did not decide in favour of Monster Energy Company in its opposition to Defensive Mark Reg. No. 5673517 for the word mark “MONSTER STRIKE” in Classes 29, 30, and 32.
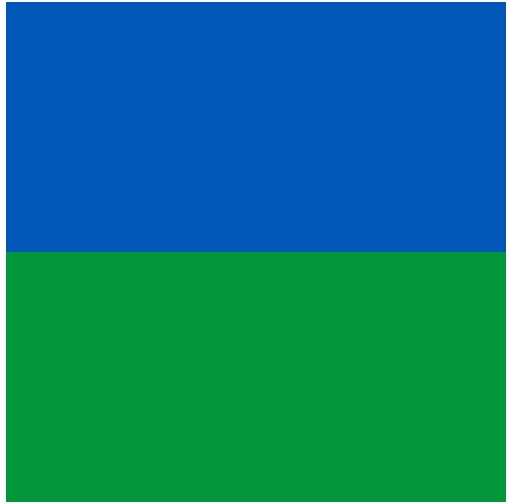
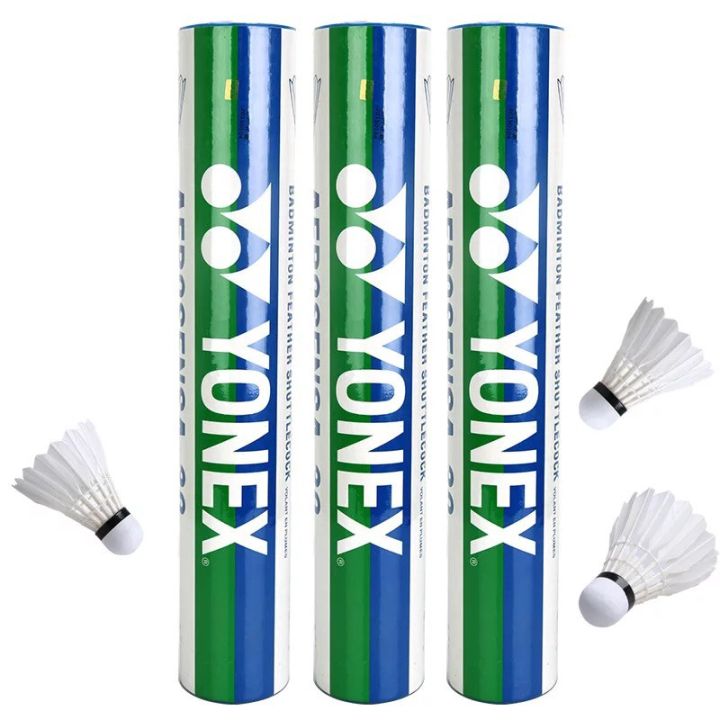
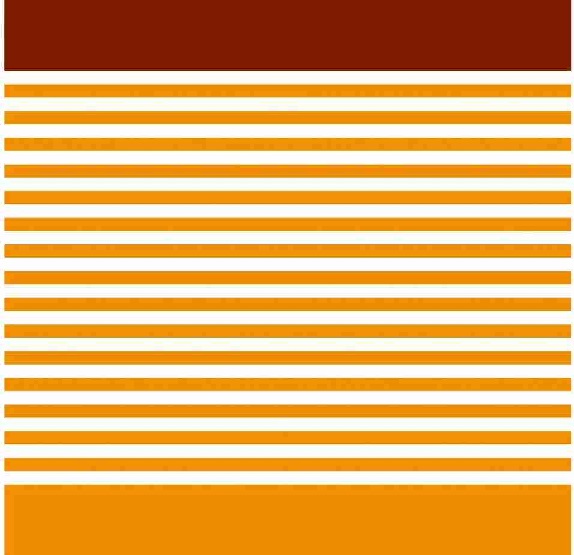
7: YONEX Scored Win in Registering Color mark
On October 21, 2025, the Japan Patent Office (JPO) granted registration of a color mark that consists of blue and green colors, filed by Yonex Co., Ltd. to use on badminton shuttlecocks by finding acquired distinctiveness of the color combination.
8: HERMES Defeated with Trademark Opposition against KIMONO TWILLY
The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition filed by Hermes International against TM Reg no. 6753650 for the word mark “KIMONO TWILLY” in Class 18, claiming a likelihood of confusion with the Hermes scarves “TWILLY”.
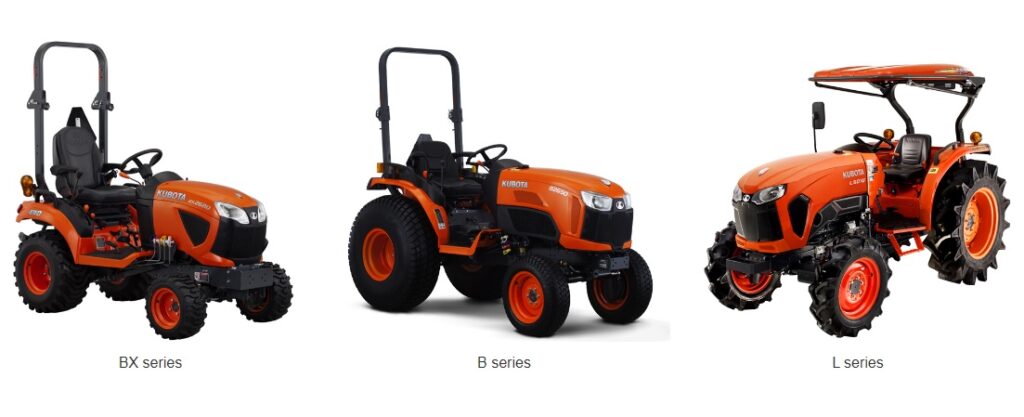
9: JPO Said No to Register Kawasaki Green Color Mark
On March 19, 2025, the Japan Patent Office (JPO) finally decided to reject a color mark application filed a decade ago by Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., which sought to register a green color used on the world-famous Kawasaki motorcycles.
10: TOMMY HILFIGER vs TOMTOMMY
The Japan Patent Office (JPO) did not side with Tommy Hilfiger Licensing B.V. in an opposition against TM Reg no. 6604265 “TOMTOMMY” due to dissimilarity and unlikelihood of confusion with “TOMMY” and “TOMMY HILFIGER”.