In a trademark dispute, similarity between “OKLOK” and “OKLOCK”, the Appeal Board of the Japan Patent Office found both marks dissimilar and reversed examiner’s rejection.
[Appeal case no. 2019-16781, Gazette issued date: March 27, 2020]
OKLOK
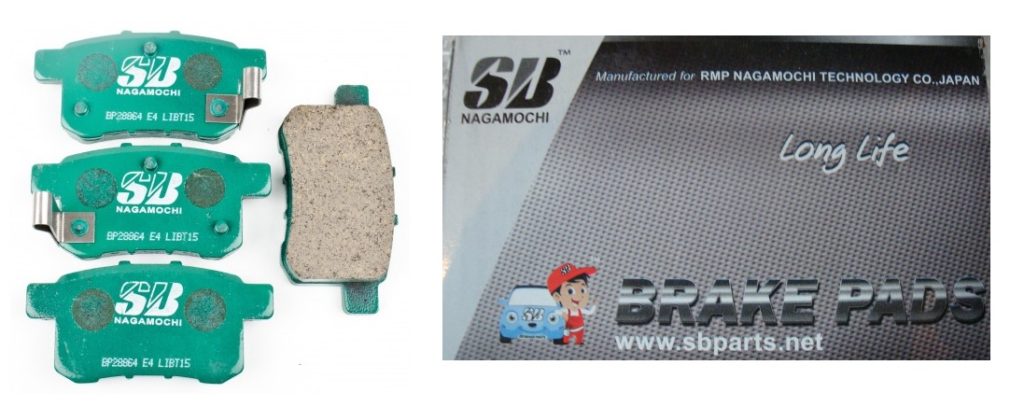
A senior mark, consisting of a word “OKLOK” in standard character, was registered on September 21, 2018 (TM Reg no. 6083192) over electric locks; electronic key fobs being remote control apparatus; anti-theft warning apparatus; other goods in class 9 by a Chinese business entity, 深圳市龙兄弟数码锁有限公司 (Shenzhen Longbrothers Digital Co., Ltd.).
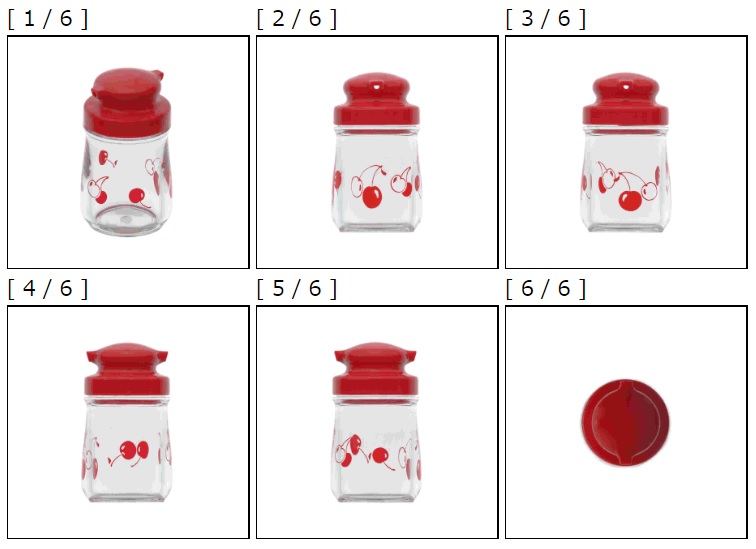
Owner has used “OKLOK” on fingerprint key less padlock, Smart Bluetooth Security Lock with USB Charge and other intelligent anti-theft devices (see below).
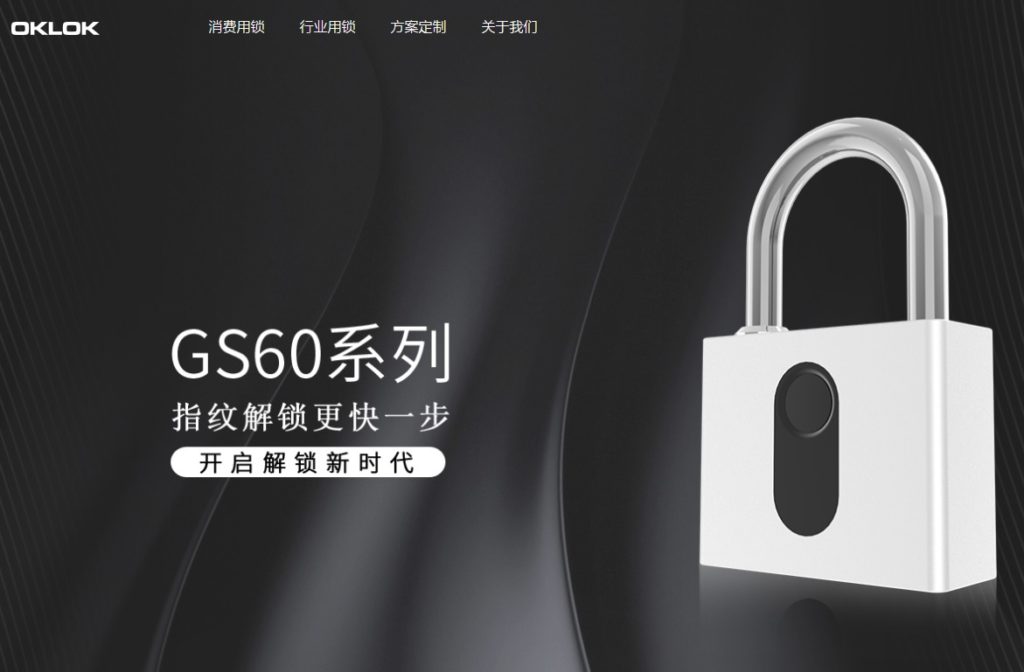
OKLOCK
Applied junior mark, consisting of a word “OKLOCK” in standard character, was applied for registration on April 3, 2019 over anti-theft locks for use on automobile steering wheels and other goods in class 12 [TM application no. 2019-47122].
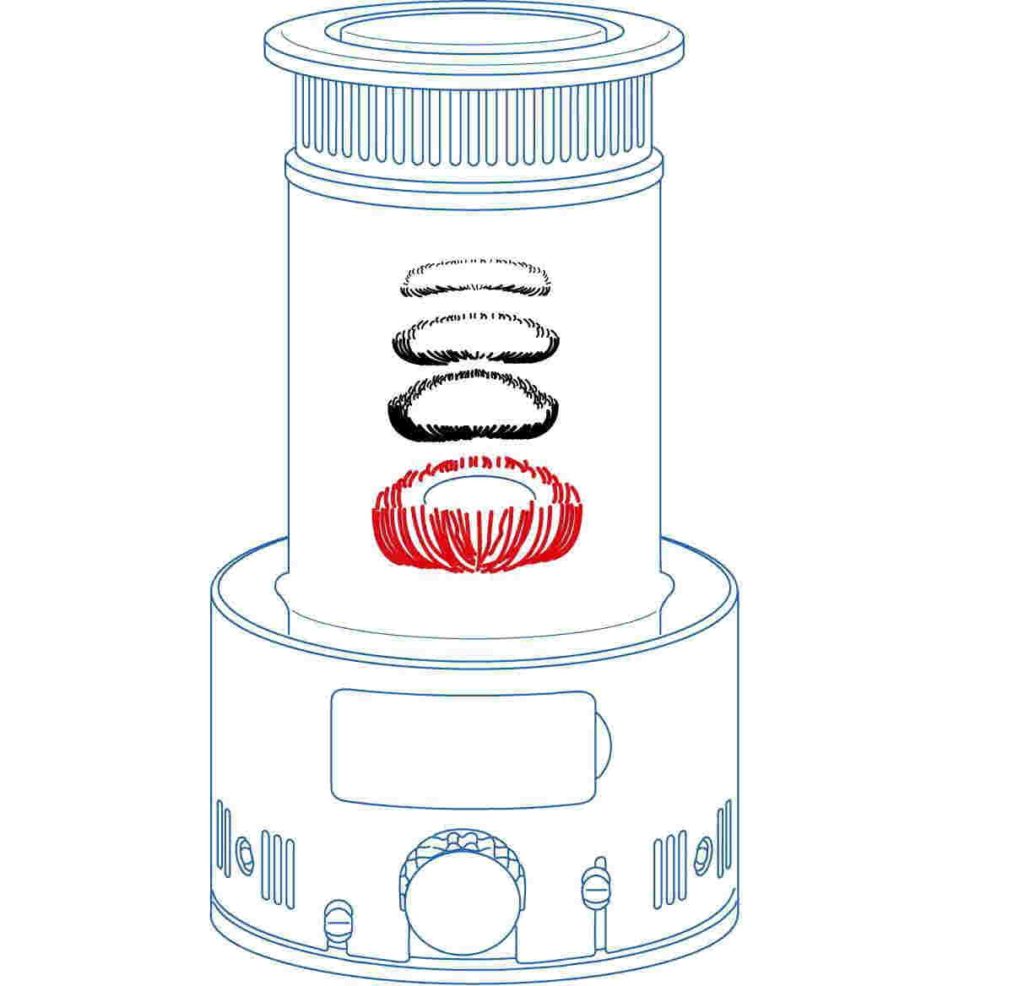
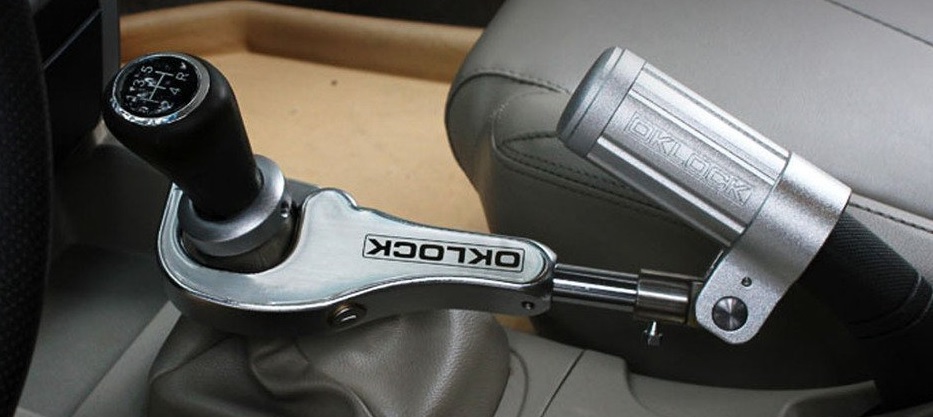
Applicant uses “OKLOCK” on car steering wheel locks and anti-theft car hand brake and gear lock (see below).


The JPO examiner rejected “OKLOCK” because of confusing similarity to “OKLOK” based on Article 4(1)(xi) of the Trademark Law.
Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit registering a junior mark which is identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
There is criterion that the examiner is checking when assessing the similarity between the marks:
- visual similarity
- aural similarity
- conceptual similarity
and taking into account all these three aspects examiner makes a decision if a mark is similar (at least to some extent) with the earlier mark and if there is a likelihood of confusion for the consumers.
Applicant filed an appeal against the rejection on December 11, 2019 and argued dissimilarity of both marks.
Appeal Board decision
In the decision, the Appeal Board held that:
From appearance, applied mark “OKLOCK” contains a letter “C” unlike the cited mark “OKLOK”. This gives rise to a distinctive impression visually in the mind of relevant consumers where respective mark consists of five or six-letter words, anything but long.
Next, applied mark is pronounces as [oʊˈkeɪ lɑːk]. In the meantime, the cited mark just gives rise to a pronunciation of [oʊˈkeɪ el ə keɪ] because relevant consumers are likely to see “OKLOK” as a combination of five alphabets and read it as each letter sounds since “OKLOK” does not appear in dictionary.
Thirdly, applied mark does not give rise to any specific meaning in its entirety even though it is perceived as a combination of “OK” and “LOCK”. Likewise, relevant consumers would not conceive any meaning from “OKLOK” and just see it as a coined word. If so, both marks are incomparable from concept.
Based on the foregoing, the Board found no reasonable ground to affirm examiner’s rejection from visual, phonetic, and conceptual points of view and decided to reverse examiner’s rejection.