In a trademark dispute pertinent to the similarity between “APLAY” and “applay”, the Appeal Board of the Japan Patent Office found both marks dissimilar and reversed the examiner’s rejection.
[Appeal case no. 2020-6380, Gazette issued date: April 30, 2021]
APLAY
A senior mark, consisting of the word “APLAY” in standard character, was registered on April 28, 2017 (TM Reg no. 5943175) over computer programs; application software; game programs for home video game machines; electronic circuits, and CD-ROMS recorded with programs for hand-held games with liquid crystal displays; electronic publications; earphones; headphones in class 9, and software as a service [SaaS]; other related computer services in class 42 by Nain Inc.
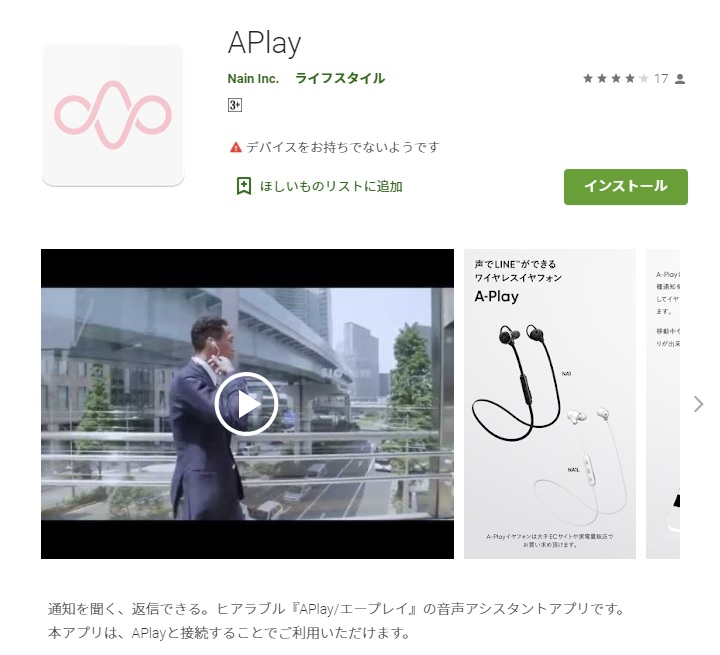
Apparently, Nain has used “APLAY” on wireless earphones and connect app for android (see below).
applay
Applied junior mark, consisting of the word “applay”, was sought for registration on August 7, 2019, over toys in class 28 [TM application no. 2019-107218] by Ed. Inter Co., Ltd.

The applicant uses the mark on wooden toys for kids (see below).
The JPO examiner rejected “applay” because of similarity to “APLAY” based on Article 4(1)(xi) of the Trademark Law.
Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit registering a junior mark that is identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
There is the criterion that the examiner is checking when assessing the similarity between the marks:
- visual similarity
- aural similarity
- conceptual similarity
and taking into account all these three aspects, the examiner would decide if a mark is similar (at least to some extent) to the earlier mark and if there is a likelihood of confusion for the consumers.
Applicant filed an appeal against the rejection on May 12, 2020, and argued dissimilarity of the marks.
Appeal Board decision
In the decision, the Appeal Board held that:
In appearance, there are differences in the third letter ‘p’, and lower case or upper-case letters. These would give rise to a distinctive impression visually in the mind of relevant consumers where the respective mark consists of five or six-letter words, anything but long.
Next, assessing the pronunciation between applied mark [ˈæpleɪ] and the cited mark [əˈpleɪ], the difference in the first sound would be anything but negligible in view of a few phonetic compositions of four sounds in total. Relevant consumers would be unlikely to confuse each sound when pronounced because of phonetical distinction in overall nuance and tone as a whole
Thirdly, the respective mark does not give rise to any specific meaning at all. If so, both marks are incomparable from the concept.
Based on the foregoing, the Board found no reasonable reason to affirm the JPO examiner’s rejection from visual, phonetic, and conceptual points of view as well as consumer perception and decided to reverse the examiner’s rejection.